Date
15/November/2023
Share
From Transactions to Transformation: The Role of Blockchain in Fintech Evolution
Traditional financial systems often grapple with issues like slow transactions, high fees, and a lack of transparency. Integrating blockchain technology into fintech operations provides a solution to these problems.
Reduced Operational Costs
Traditional systems involve multiple entities, each charging fees for their services, especially in cross-border payments. Blockchain's peer-to-peer transactions and decentralized protocols streamline processes, reducing costs for both fintech companies and customers.
Enhanced Service Availability
Blockchain empowers fintech companies to operate without geographical restrictions. Decentralized applications, cryptocurrencies, and smart contracts enable clients to access financial services globally, 24/7, overcoming regulatory barriers and technical limitations.
Improved Security
Data security and privacy protection are paramount in fintech. Blockchain's decentralized nature, encryption techniques, and immutability enhance cybersecurity by eliminating single points of failure, securing data transmission, and preventing unauthorized alterations. It significantly mitigates the risk of cyberattacks and fraud.
Enhanced Traceability
Traditional financial systems often lack transparency and create traceability challenges due to centralization and multiple intermediaries. Blockchain's distributed ledger provides unparalleled traceability, enabling easy tracking, verification, and auditing of fintech activities.
Faster Processing
Blockchain accelerates settlement times by reducing manual processes and intermediaries. It streamlines verification and authorization procedures, resulting in quicker and more cost-effective financial operations.
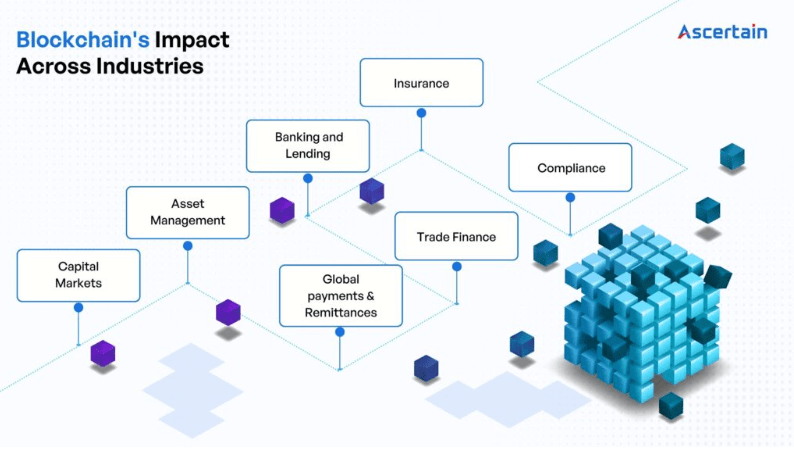
Let's explore how it's transforming key sectors:
- Capital Markets:
Blockchain streamlines capital market activities by eliminating single points of failure, facilitating capital market operations, digitizing workflows, and enabling the tokenization of assets for increased liquidity and fractionalized ownership.
- Asset Management:
Automates fund launches, enhance stakeholder engagement, supports the digitization of portfolios, offers customizable privacy settings, and ensures voting and other shareholder rights are programmed into digital assets.
- Global Payments and Remittances:
It enables rapid and secure domestic and cross-border payments, real-time gross settlement, and digitized KYC/AML data for authentication.
- Banking and Lending:
Blockchain transforms core banking services, including document authentication, credit prediction, syndicate formation, and collateralization of assets.
- Trade Finance:
Blockchain digitizes the entire lifecycle, providing security and efficiency. It offers authenticated documentation, asset digitization, efficient financing structures, and consistent financing vehicles for the entire trade.
- Insurance:
Blockchain enhances insurance by securely streamlining data verification, claims processing, and disbursement. It facilitates automated claims processing, parameterized contracts, and tokenized reinsurance markets.
- Compliance:
Blockchain eases regulatory compliance by programming unique governance and compliance attributes into digital assets. It streamlines processes, automates data verification and reporting, and enforces incentive structures for improved network governance.
Blockchain technology has found numerous use cases in financial services, revolutionizing the sector. Here are some prominent examples:
Cryptocurrencies: The most well-known use case is cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum. Blockchain enables the creation, transfer, and secure storage of digital currencies, eliminating the need for intermediaries like banks.
Smart Contracts: Smart contracts are self-executing agreements with the terms of the contract directly written into code. They automate tasks and processes, reducing the need for intermediaries in various financial transactions.
Cross-Border Payments: Blockchain simplifies and accelerates cross-border payments by eliminating multiple intermediaries, reducing fees, and ensuring faster settlement times.
Identity Verification: Blockchain offers a secure and transparent way to manage and verify customer identities, reducing the risk of identity theft and fraud.
Asset Tokenization: Financial assets, such as real estate or artwork, can be tokenized on the blockchain, allowing for fractional ownership and easier transfer of ownership.
Supply Chain Finance: Blockchain enhances transparency and traceability in supply chains, making it easier to access financing based on the provenance of goods.
Credit Scoring: Blockchain can enable more accurate and inclusive credit scoring by using a person’s transaction history as a basis, particularly beneficial for the unbanked or underbanked populations.
Regulatory Compliance: Blockchain technology helps financial institutions comply with increasingly complex regulations by providing a tamper-proof record of transactions.
Securities Trading: Blockchain facilitates the issuance, trading, and settlement of securities, reducing the need for intermediaries and enhancing market efficiency.
Remittances: Blockchain solutions can significantly reduce the cost and time associated with remittances, benefiting the unbanked and underbanked populations.